
XRF Metal Sorting Explained: How X-Ray Fluorescence Works in Recycling
18 Dec 2025
Recycling metal efficiently requires accurate material identification and separation. One of the most effective technologies for this purpose is X-ray fluorescence (XRF) metal sorting. XRF allows recycling plants and machine builders to identify metals and alloys in real-time, enabling high-throughput sorting, reducing contamination, and optimising resource recovery.
In this article, we explain how XRF works, the applications in recycling, and best practices for machine builders and system integrators.
What Is XRF Metal Sorting?
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is a non-contact, non-destructive analytical technique used to determine the chemical composition of metals. When a material is exposed to X-rays, it emits secondary (fluorescent) X-rays that are characteristic of the elements present.
XRF sensors detect these emitted X-rays and quickly identify:
- Metals (iron, copper, aluminum, etc.)
- Alloys (brass, bronze, stainless steel)
- Precious metals (gold, platinum)
- Rare earth elements
This information allows sorting machines to separate materials accurately and efficiently.
How XRF Metal Sorting Works in Recycling
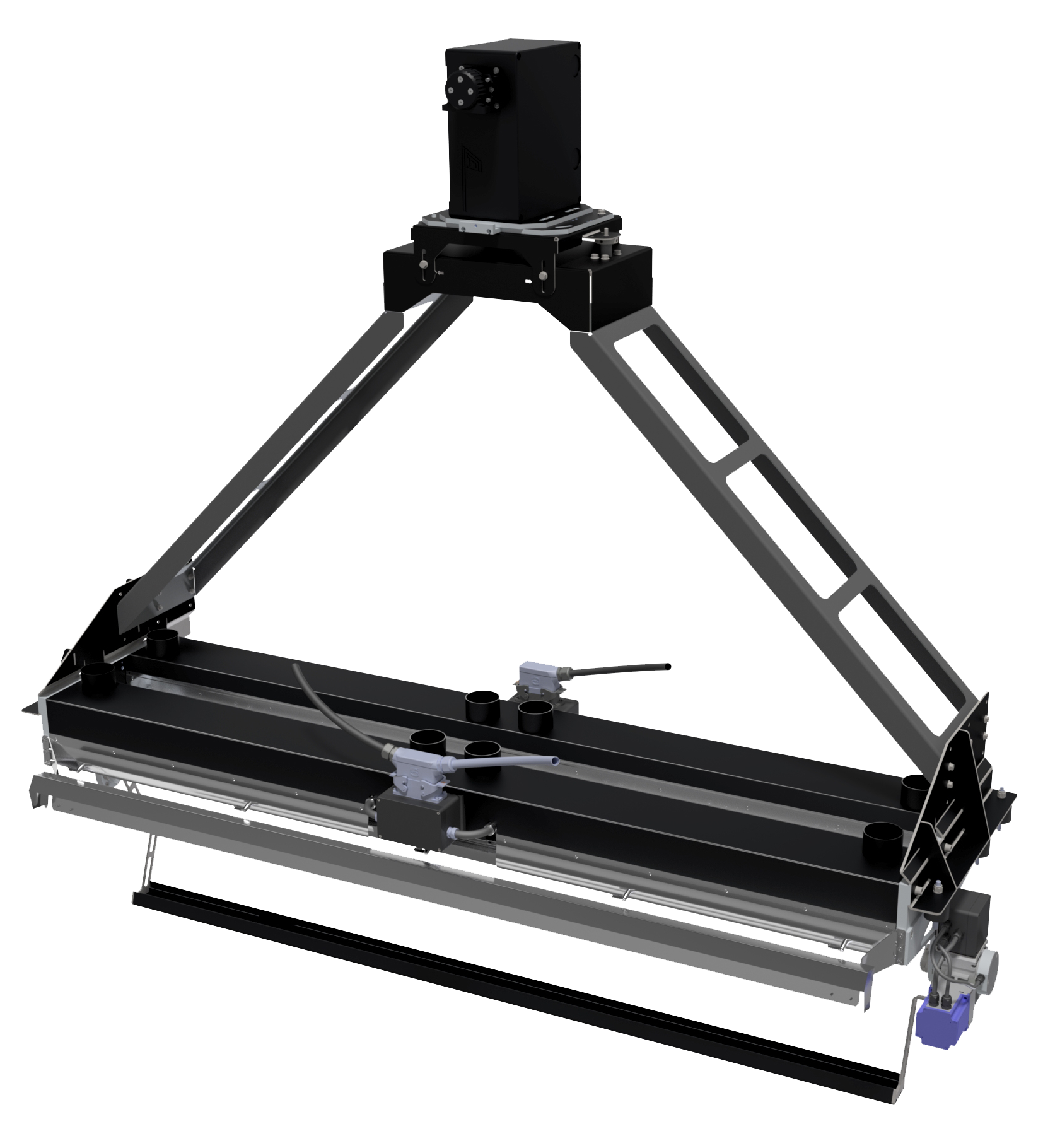
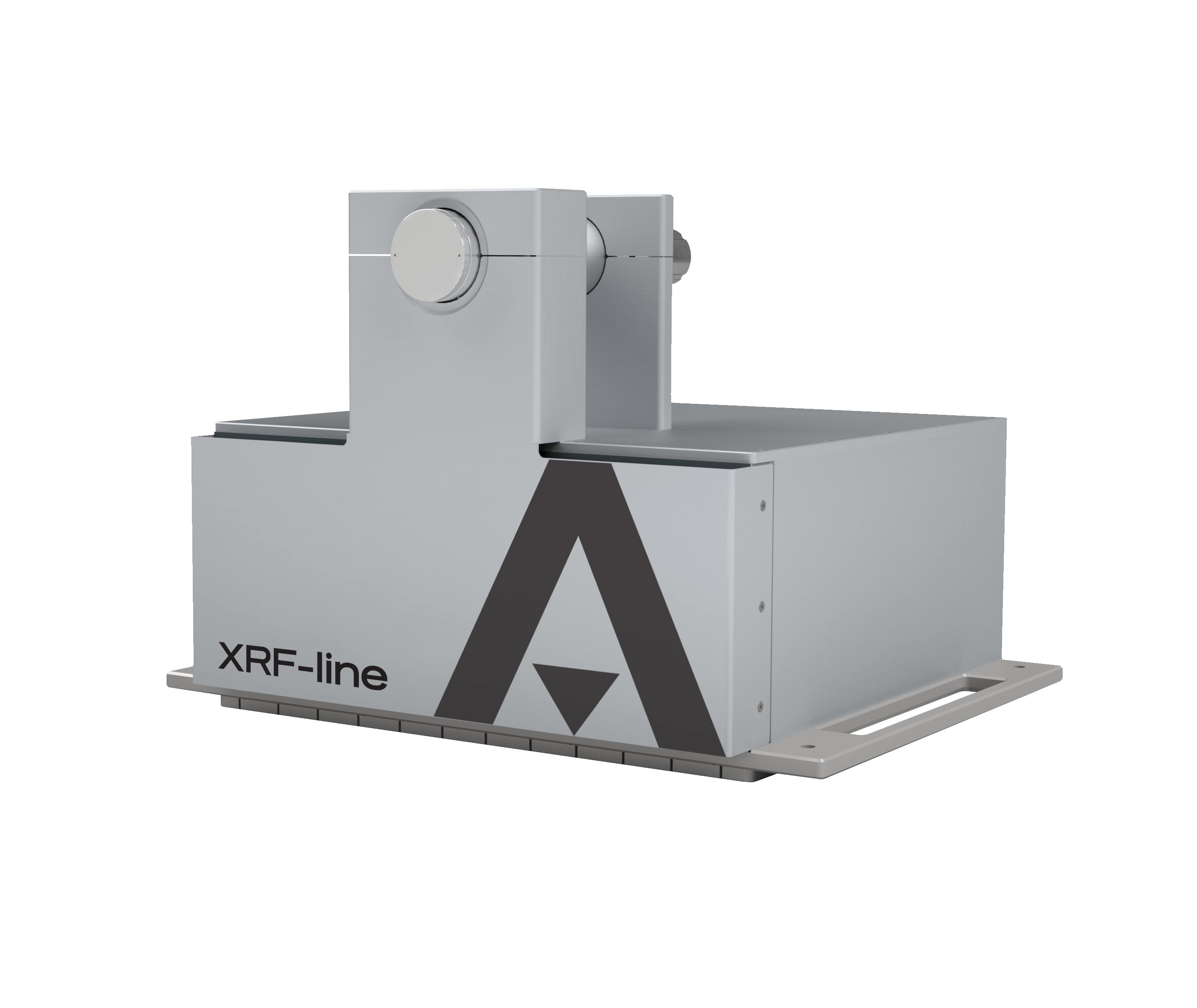
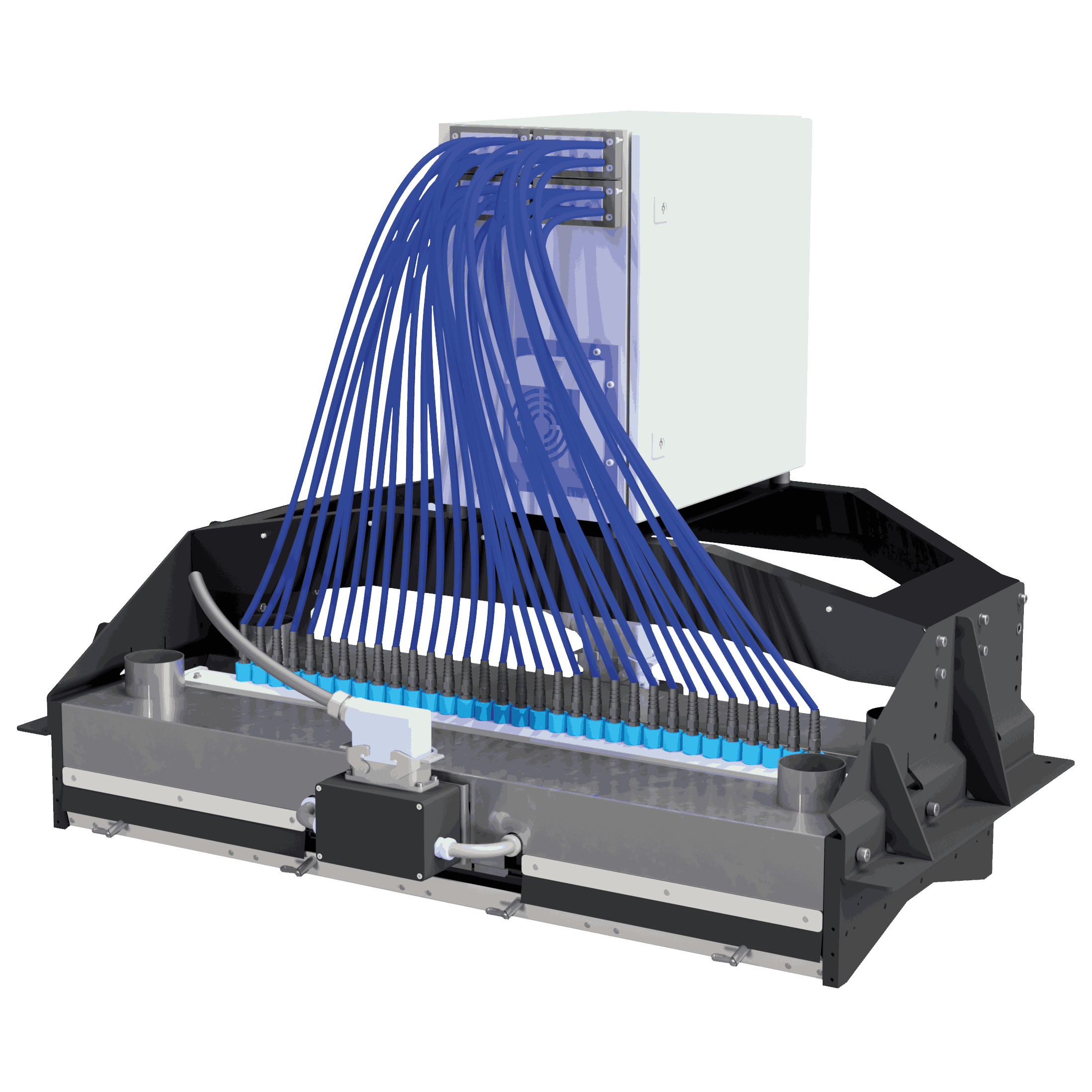
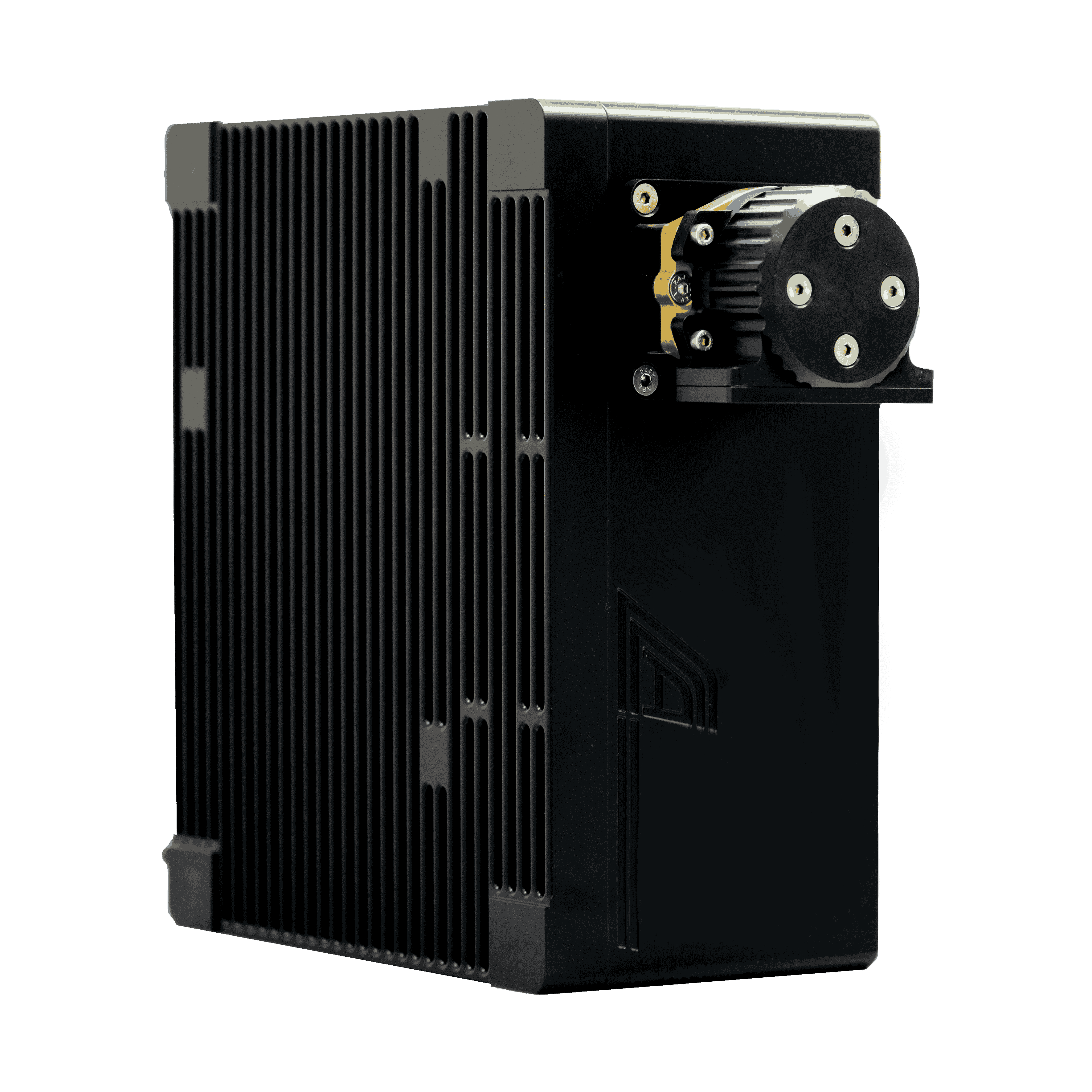
XRF metal sorting systems, such as the XRF-line, are designed to handle moving conveyor belts in industrial recycling facilities. Here’s how the process works:
- Conveyor Transport: Metal pieces or streams move along a conveyor at high speed.
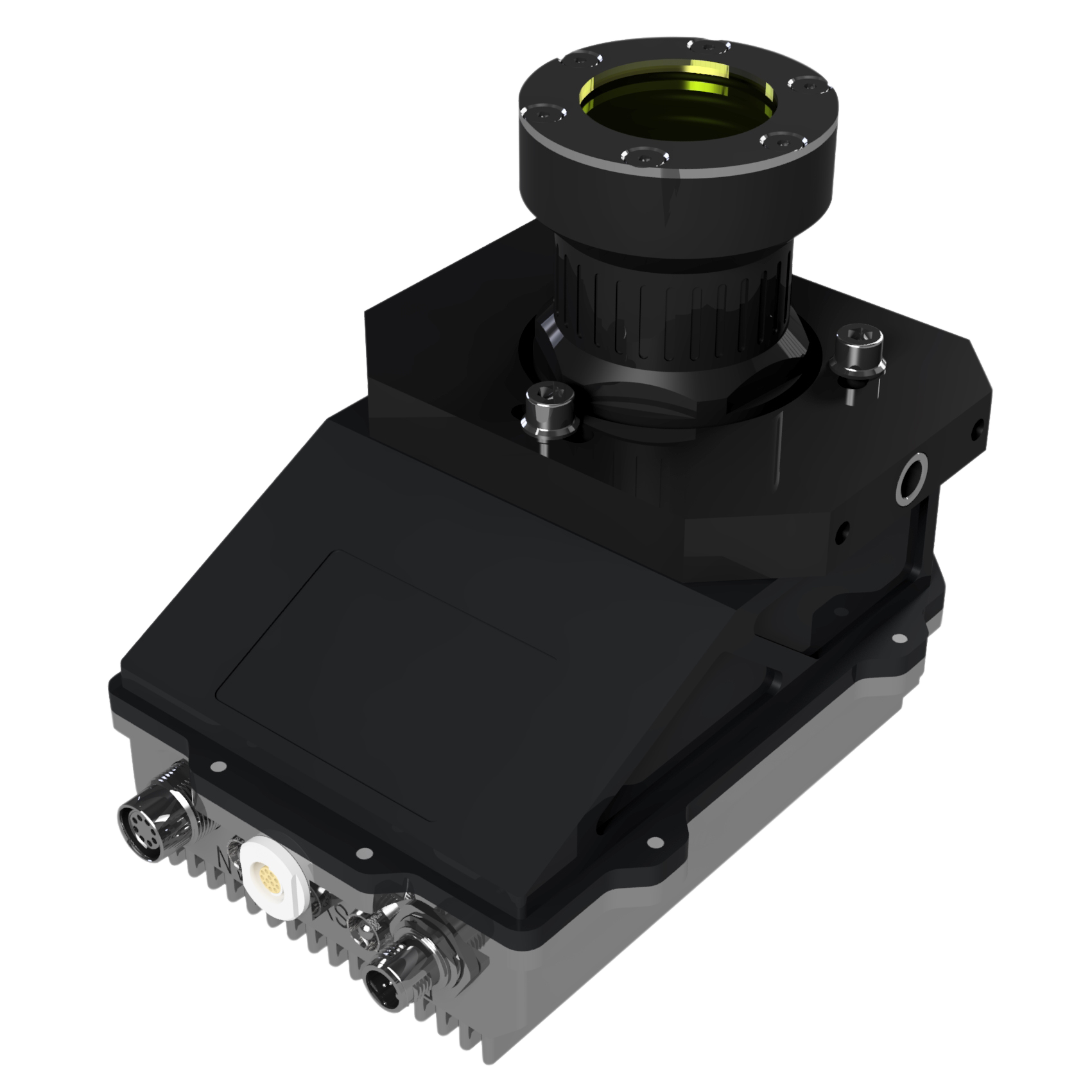
- XRF Sensor Detection: X-ray detectors, often Silicon Drift Detectors (SDD), analyse the emitted fluorescence from each piece.
- Data Processing: Integrated software evaluates the elemental composition in real-time.
- Sorting Action: Based on the analysis, the system can activate blow-off valves or diverters to separate metals by type or alloy.
The result is precise, high-speed metal separation, suitable for scrap, WEEE, incinerator bottom ash (IBA), and other recycling streams.
Applications of XRF in Recycling
XRF metal sorting is versatile and widely used in recycling:
- Sorting impurities: Remove unwanted metals like lead, tin, or glass from material streams.
- Sorting by main components: Separate iron, copper, aluminum, and other common metals.
- Alloy classification: Identify brass, bronze, stainless steel, and specialised alloys for higher-value recycling.
- Precious metals detection: Recover gold, platinum, or other valuable metals from electronic waste.
- Incinerator Bottom Ash (IBA): Extract metals efficiently from municipal waste residue.
By integrating XRF into sorting systems, recycling plants can maximise material recovery and reduce landfill waste.
Advantages of XRF Metal Sorting
- Non-Destructive Analysis: Metals remain intact during detection.
- No Sample Preparation Needed: Materials can be analysed directly on the conveyor belt.
- Real-Time Sorting: High-speed sensors provide results at up to 100 Hz.
- High Accuracy: Detects alloys and trace elements that optical sensors cannot distinguish.
- Process Control: XRF systems can monitor average metal composition to optimise upstream or downstream processes.
Best Practices for Machine Builders
For OEMs and integrators designing XRF-based sorting systems:
- Choose the right detector: Silicon Drift Detectors (SDD) are standard for industrial XRF applications.
- Integrate industrial PCs: Real-time data processing ensures accurate sorting.
- Ensure environmental robustness: Dust-proof, waterproof designs (IP-rated) allow continuous 24/7 operation.
- Use intuitive software: Operator and expert modes help with detector configuration, system monitoring, and statistical analysis.
Following these guidelines ensures that XRF-line systems deliver consistent performance and help recycling plants achieve high throughput and quality.
Conclusion
XRF metal sorting is a critical technology for modern recycling. By using X-ray fluorescence, machine builders and recycling facilities can identify metals and alloys with precision, sort materials efficiently, and maximise resource recovery.
Whether it’s scrap steel, electronic waste, or precious metals, XRF systems provide a reliable, high-speed, and non-destructive solution for metal sorting applications.
Call to Action:
Ready to optimise metal sorting in your recycling process? Request more information about LLA’s XRF-line system today.









































 Previous Post
Previous Post
