Home / How it works / Spectroscopic Methods
Spectroscopic Methods
How it works?
Our measuring systems are based on various spectroscopic methods. By evaluating the measurement data we gather using chemometric methods, we obtain chemical information and then make them available to you as a result.
The characteristic light spectrum of a sample is generated by method-dependent physical mechamisims as outlined below.
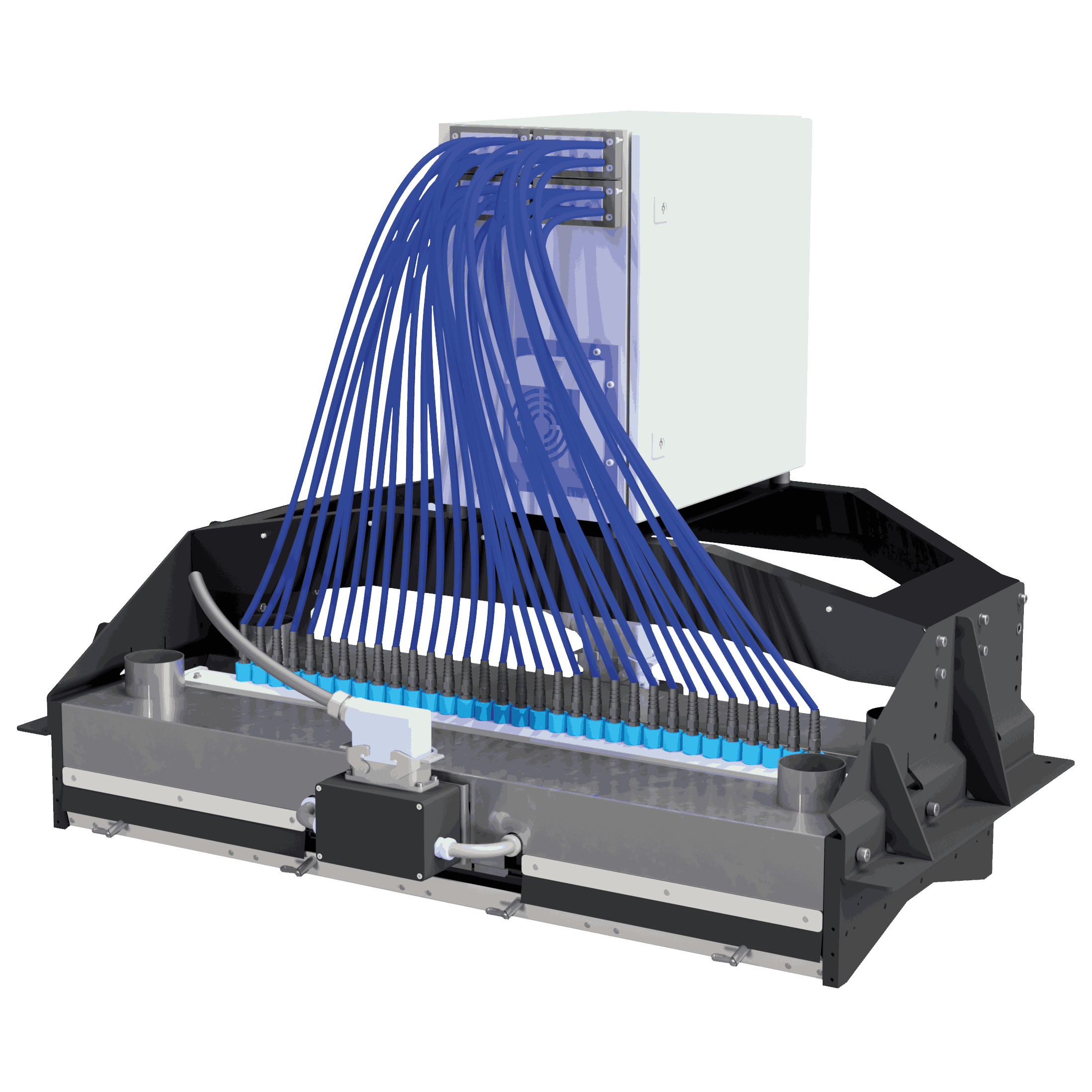
The recording of the spectrum for each location point is through the functionality of our measurement systems which is detailed in Spectra Measurement.

VIS/NIR - excitation of electrons
Spectral range: 350 nm – 950 nm
VIS uses visible light to measure the transitions of excited electrons in the samples under investigation. The light that is reflected, and therefore not used during these transitions, has a characteristic colour. For this reason, the spectral change between the absorbed and reflected light can be used for colour determination. We use this effect to detect colour and pattern differences in the long-wave UV and VIS/NIR range.
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS:
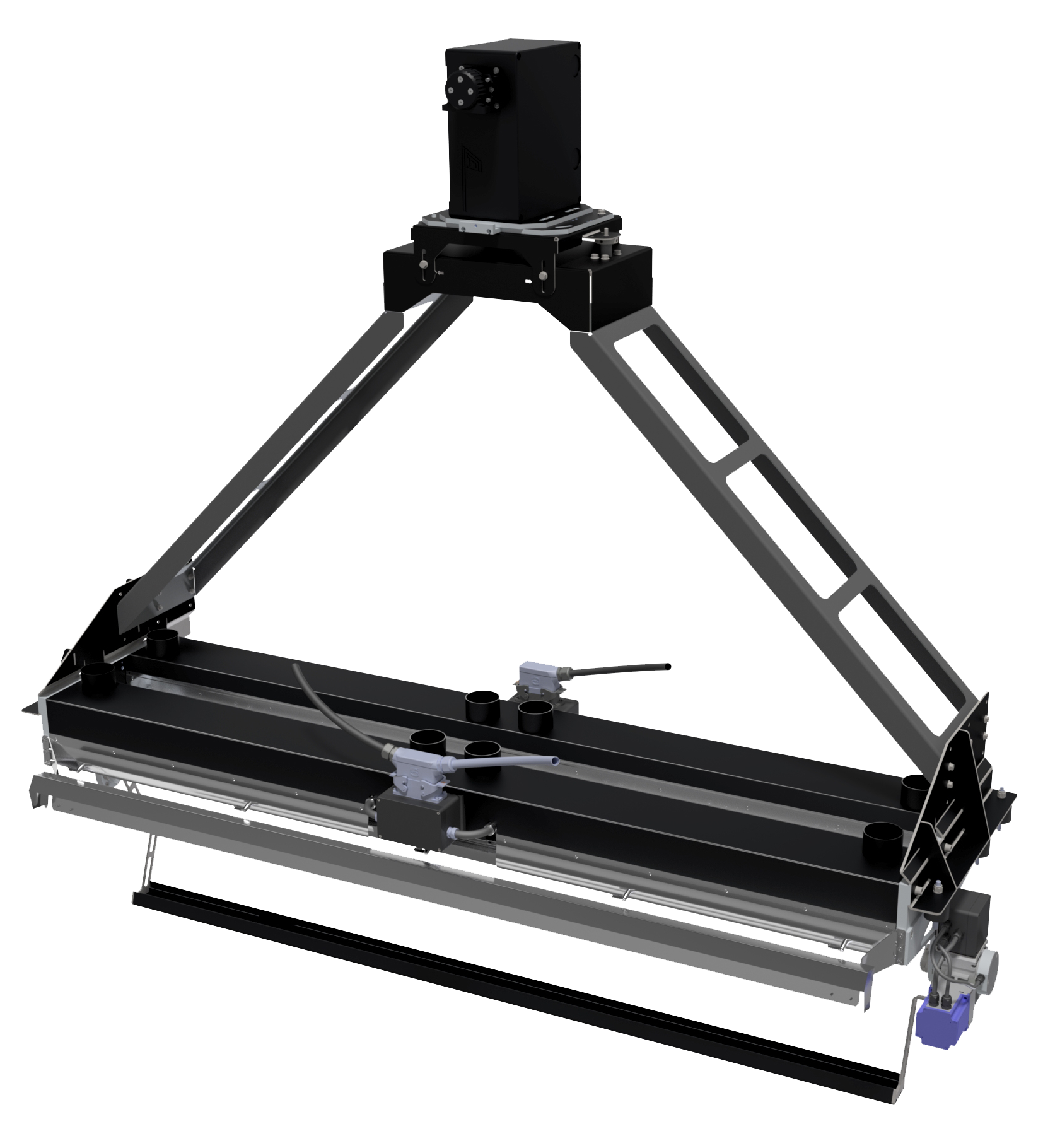
KUSTA
Hyperspectral cameras
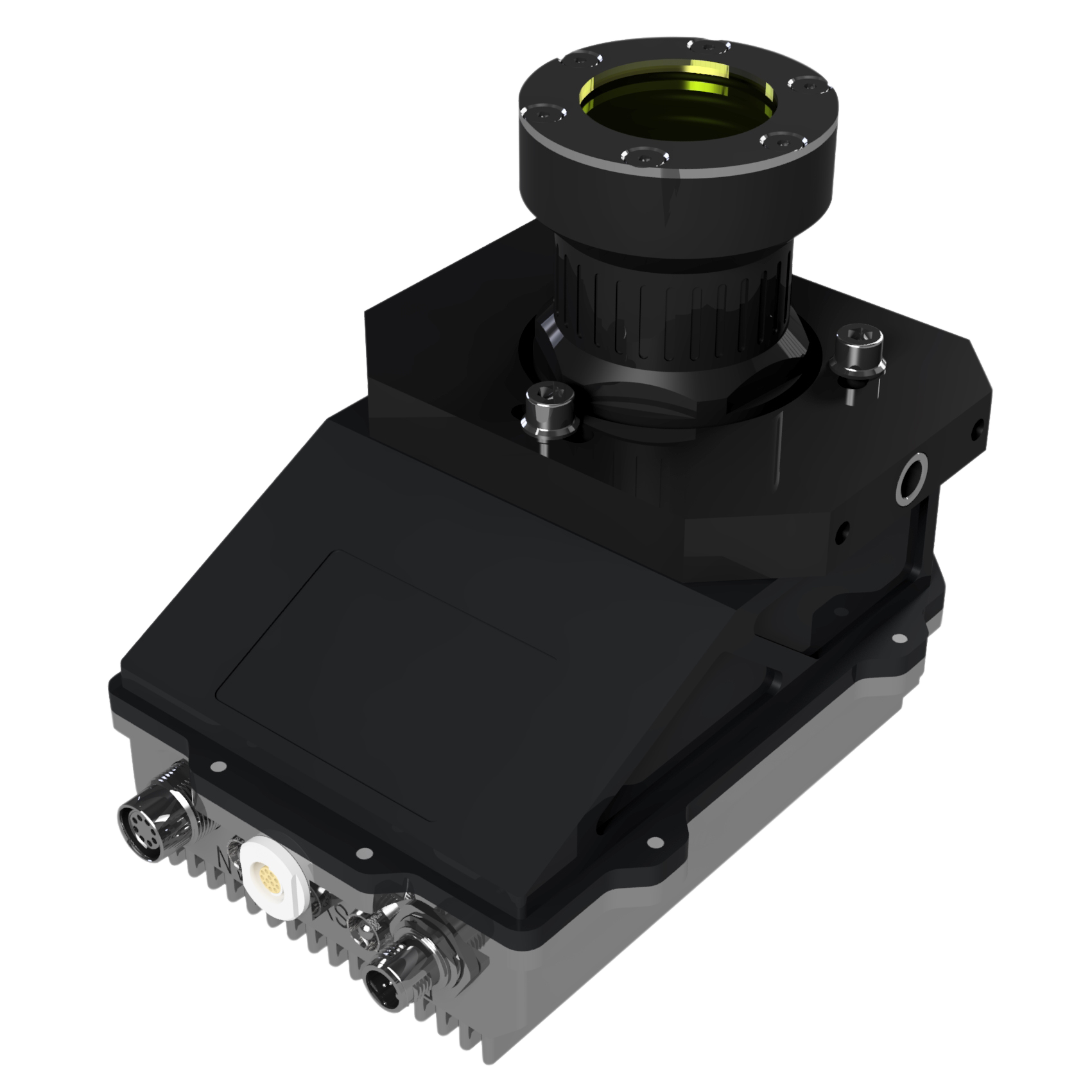

LineScan-RGB
Universal line scan colour camera
NIR/SWIR - vibrational spectroscopy - molecular spectroscopy
Spectral range: 950 nm – 2190 nm
Light in the near-infrared range (NIR) is used to excite molecular vibrations in the samples under investigation. This mainly affects C-H, N-H, and O-H bonds. The excitation of vibrations cause parts of the spectrum to be absorbed, resulting in so-called absorption bands. This spectral change between the absorbed and the reflected light is measured and used for evaluation.
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS:

X-ray radiation - x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF)
Spectral range: 0.04 nm – 0.4 nm
X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF) is based on the following principle: High-energy x-rays excite electrons from the inner orbitals in such a way that they leave the atom. When the resulting gaps are filled by electrons from outer orbitals, characteristic element-specific x-rays are emitted. These are used to analyse the sample.
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS:

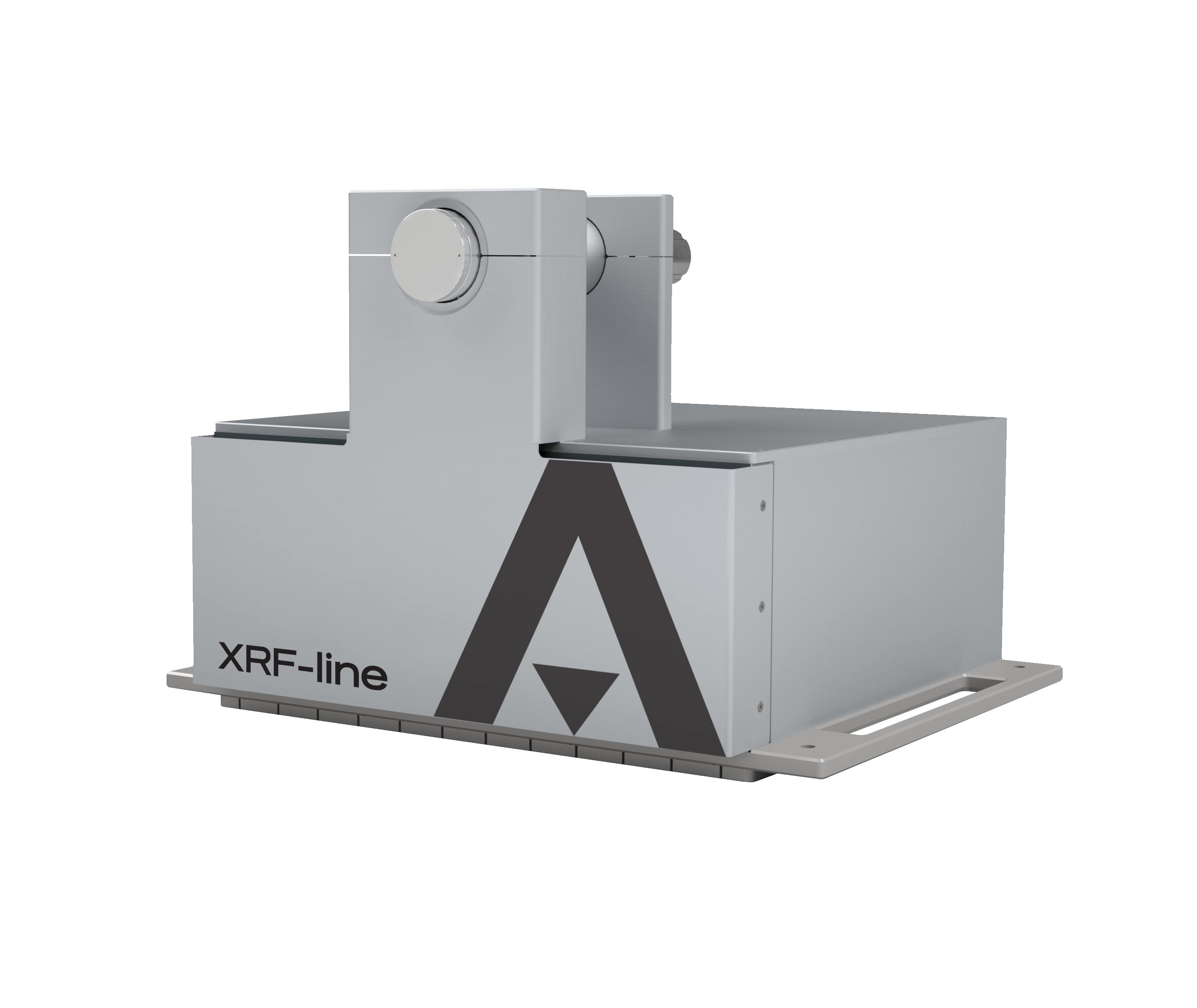
XRF-line
X-ray fluorescence analyser